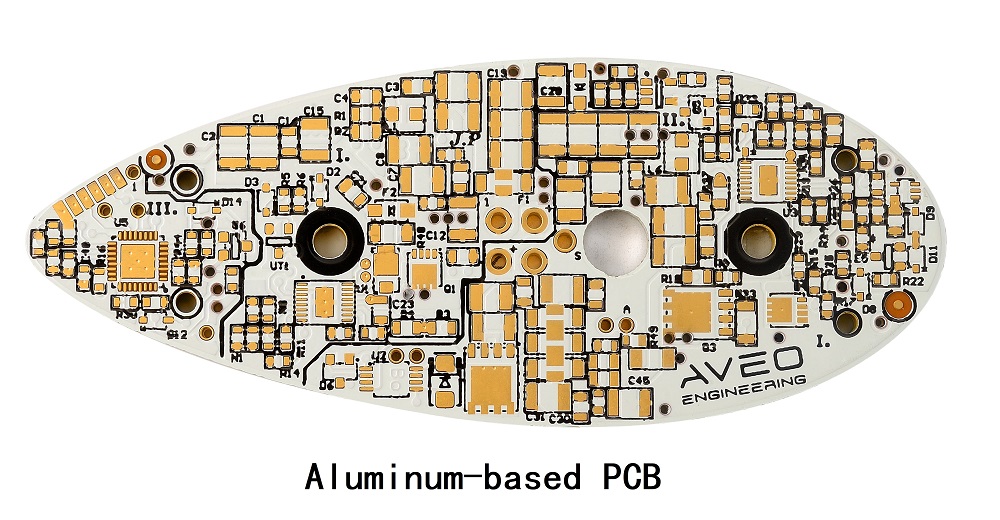
Aluminum PCB
Aluminum PCBs are widely used electronic boards with comparatively better heat dissipation properties. The aluminum core cools down the components of the product, thereby improving its performance. These are eco-friendly, light, and strong PCBs and hence appropriate to be used in audio equipment, power supplies, and lighting products such as LED lighting.
What is an Aluminum-based PCB?
Aluminum-based PCBs are the most widely used metal core PCBs. An Aluminium-based PCB has a core made of Aluminium, not regular FR4 material, making it a very useful way to dissipate heat and hence helps cool components of an electronic board for improved performance of the product.
Advantages of an Aluminium-based PCB
- Eco-Friendly: Aluminum is non-toxic and recyclable. The manufacturing process helps in saving energy and is easy to assemble. Further, the use of aluminum in the manufacture of PCBs is very eco-friendly.
- Excellent Heat Transfer: High temperatures may affect electronic devices quite adversely. There is, hence, a need to employ materials in ways that allow for efficient heat dissipation. Aluminum efficiently transfers heat away from elements that generate heat or critical parts, minimizing their possible dangerous effect on the circuit board.
- Durable: Aluminum is strong, tough, and durable, unlike ceramic or glass fiber substrates, reducing the possibility of damage due to accidents during production, handling, and day-to-day use.
- Lightweight: Using aluminum improves the durability and strength of products without adding unnecessary weight.
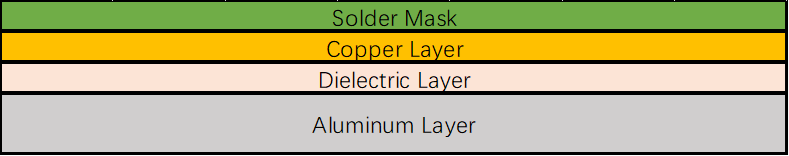
Structural Features of an Aluminum PCB
Circuit Copper Layer: The circuit copper layer is usually made of electrolytic copper foil, which is etched to form the printed circuit applied for component assembly and connections. As compared to conventional FR4, the aluminum substrate PCB can stand higher currents at the same thickness and line width.
Dielectric Insulation Layer: The dielectric insulation layer is a critical technology in aluminum PCBs that serves three functions: bonding, insulation, and heat conduction. The insulation layer with enhanced thermal conductivity ensures improved heat dissipation from the components. Reduced working temperature leads to increased power handling, smaller volume, longer lifespan, and higher power output.
Metal Substrate: The thermal expansion coefficient, thermal conductivity, strength, hardness, weight, surface condition, and cost of an insulated metal substrate are some of the parameters that will determine the metal.
Normally applied materials include 6061, 2052, and 1060, with the main applications being aluminum-based substrates for cost-effectiveness and optimum technical performance. However, copper, stainless steel, iron plate, or silicon steel plate may be used for further increases in thermal conductivity or mechanical/electrical enhancements.
Structure type of Aluminum PCB
One Layer Aluminum PCB with Single Component Mounting Side:
It is the simplest and largest manufacturing quantity. Circuits are directly etched onto the copper layer of the aluminum laminate board. The heat from components flows outward via the copper layer to the PP layer and then the aluminum layer.
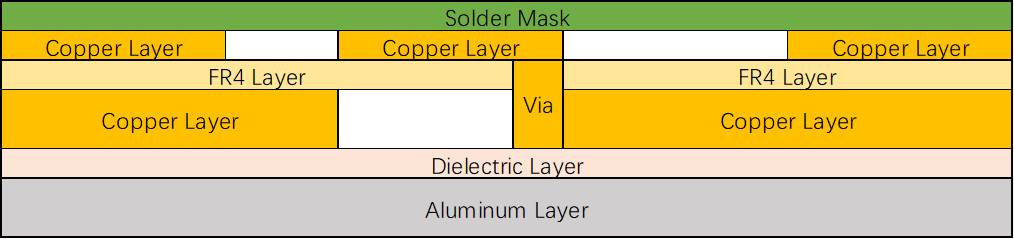
Two-layer Aluminum PCB with single component mounting side:
This variant includes two copper layers and PP layers. The heat transfers from the components to the first copper layer, the first PP layer, the second copper layer, the second PP layer, and the aluminum layer.
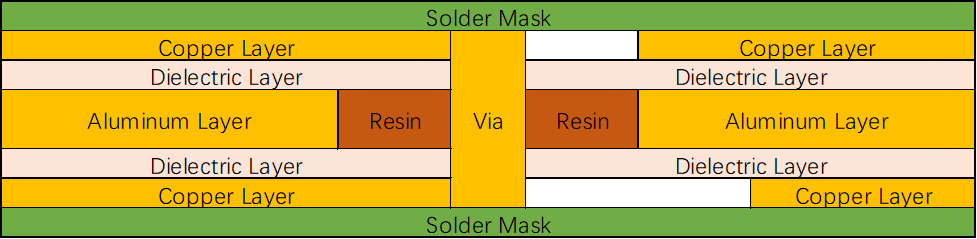
Two-layer Aluminum PCB with Dual Component Mounting Sides:
When single-sided PCBs become too small to hold all the circuitry, aluminum PCBs can be designed as double-sided. Both a two-layer FR4 PCB and an aluminum two-layer PCB with dual component mounting sides have a similar structural design. The resin fills the space between PTHs and the aluminum base. The heat from the components is transferred firstly to the copper layer, then to the PP layer, and finally to the aluminum layer.
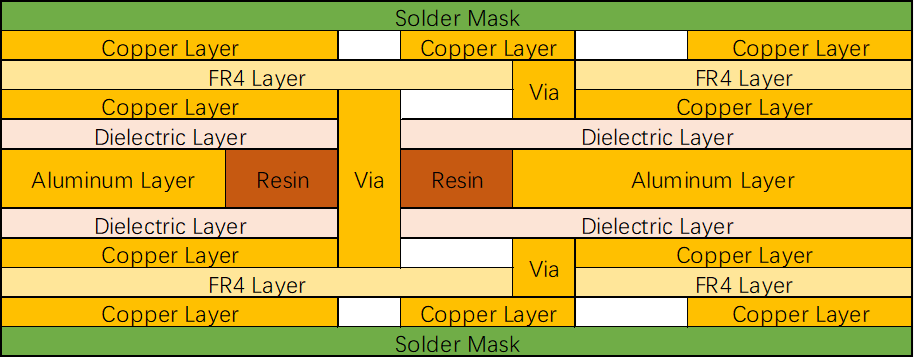
Four-layer Aluminum PCB with dual component mounting sides.
It has two copper layers and PP layers. The heat is conducted from the components to the outer copper layer, then to the first PP layer, further to the second copper layer, followed by the second PP layer, and finally to the aluminum layer. Due to this complex path, a four-layer PCB has lower thermal conductivity compared to a single-layer PCB and a two-layer aluminum PCB with dual component mounting sides.
Applications of Aluminum PCBs
- Audio Equipment: Used in input amplifiers, output amplifiers, balanced amplifiers, audio amplifiers, preamplifiers, and power amplifiers.
- Power Supply: The Supply is utilized in switch regulators, DC/AC converters, SW regulators, etc.
- Communication Electronic Devices: Used in high-frequency amplifiers, filtering devices, and transmission circuits.
- Office Automation Equipment: Used in motor drivers and related automation systems.
- Automobiles: It finds its use in electronic regulators, ignition systems, power controllers, etc.
- Computers: The CPU boards, floppy drives, power supplies, etc.
- Power Modules: Inverter, solid-state relay, rectifier, etc,
- Lamps and Lighting: With energy-saving lamps becoming increasingly popular, there are all kinds of colorful LED energy-saving lamps, most of which have an aluminum PCB inside. Thus, aluminum PCBs are widely applied in LED lighting products.
How to Calculate the Thickness of Aluminum Layer
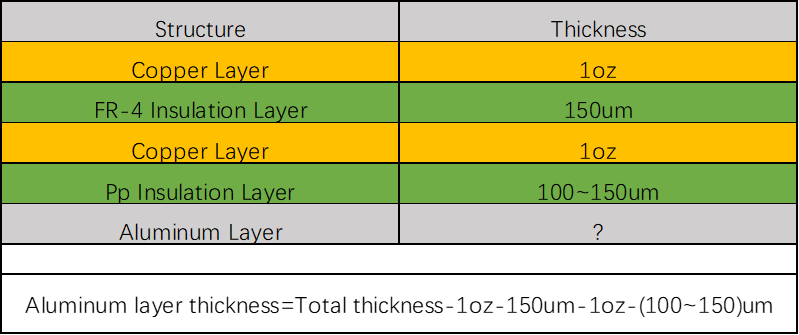
For example, the aluminum base at the bottom of the laminate can be simply calculated if the copper thickness is 1 oz and the substrate is a 2-layer aluminum PCB. In general, every one of the parameters listed above is the same. The customer's chosen plate's thickness is subtracted from the thickness of the other layers to determine the aluminum base's thickness.
Storage Conditions for Aluminum PCBs
Aluminum PCBs have to be kept in a dark, dry place to avoid moisture absorption, yellowing, and darkening. Use within 48 hours after unpacking will guarantee integrity and performance.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Solder mask, or solder resist, is the polymer layer on PCBs that protects against oxidation, short circuits, and solder bridges. Types include LPI, dry film, and epoxy, chosen based on design, application, and cost.
Green PCBs reduce visual fatigue, enhance error detection, and are cost-effective due to military influence and industry standards. However, other colors like red, blue, black, and white are also available for specific needs.
PCB prototyping is vital for testing and refining electronic circuits before mass production, ensuring performance and feasibility using methods like etching, milling, and 3D printing.