What is Cable Assembly?
Cable assemblies are essential components that ensure reliable power and data transmission across diverse industries by integrating multiple cables into custom-engineered solutions.
In today's fast-paced, technology-driven world, the seamless transfer of power, data, and signals is crucial. Although unseen and mostly unbeknownst to the average user, cable assemblies serve as a major component in our interconnected systems. Cable assemblies form the backbone of electronic and communication infrastructures. Understanding their value and applications begins with knowing the different types, major benefits, manufacturing processes entailed, and their various uses across several industries.
Understanding Cable Assemblies
A cable assembly, also commonly referred to as a cable harness or wiring assembly, is a preassembled group of wires or cables with connectors at each end. Unlike simple, standalone cables, cable assemblies are engineered toward specific electrical, mechanical, and environmental requirements. This custom-designed configuration facilitates effective and reliable power and signal transmission across a wide range of devices and systems.
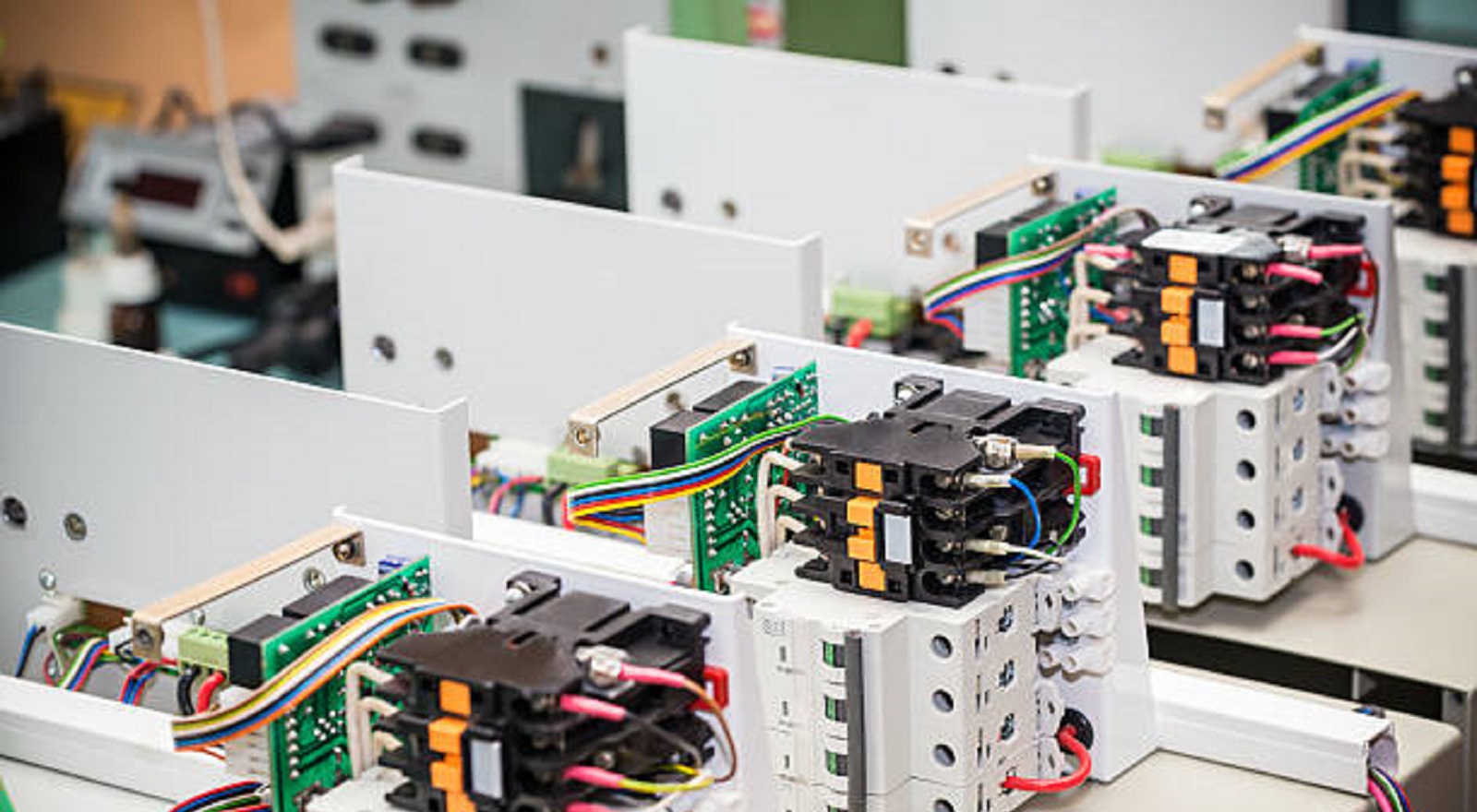
Cable assemblies act like the nervous system of electronic devices, and are designed to meet advanced criteria which include:
Electrical Performance Requirements: Optimized for specific voltage, current, and signal requirements.
Spatial Constraints: Designed to fit within the complex, often confined spaces of modern electronic devices.
Environmental Resilience: Built for temperature fluctuations, humidity, vibration, and other conditions.
Regulatory Compliance: Conforms with industry regulations and standards, essential in ensuring safety and reliability.
Cable assemblies offer enhancements in organization, ease of installation, and system dependability by integrating many cables within a single, coherent unit. All these qualities make cable assemblies indispensable in many sectors.
Types of Cable Assemblies
Cable assemblies are broadly varied, with several types designed for specific applications:
Coaxial Cable Assemblies: Constructed specifically for the transmission of signals in high frequencies with minimal interference. Their general structure consists of a central conductor, insulating layer, conductive shield, and outer jacket. These assemblies are ideal for broadcast equipment and wireless communication systems.
Ribbon Cable Assemblies: These are characterized by multiple parallel wires that give a flat, ribbon-like appearance. The compact design makes these appropriate for internal computer and printer mechanisms, allowing for ease of conductor identification while offering flexible termination options.
Molded Cable Assemblies: Feature cables encased in molded plastic or rubber at connector points, providing enhanced protection and strain relief. Commonly utilized for consumer electronics and medical devices where durability is paramount.
RF/EMI Cable Assemblies: These are intended for radio frequency applications, maintaining signal integrity within high-frequency environments due to excellent EMI shielding and minimum loss of signal.
LED Cable Assemblies: Optimized for low-voltage DC power applications, often incorporating power and control lines for architectural and automotive lighting systems.
Circular Connector Cable Assemblies: Fitted with round, multi-pin connectors that provide strong, often waterproof connections. These assemblies are ideal for industrial machinery and military equipment.
Data and Video Cable Assemblies: High-speed digital signal transmission requires appropriate cable assemblies, which use different types of connectors: USB, HDMI, DisplayPort, and others. They are crucial for computers and audio-visual equipment to ensure high bandwidth for fast data transfer.
Power Cable Assemblies: Configured to safely transmit electrical power, featuring high current-carrying capacity with robust insulation, very necessary in industrial machinery and the charging system of electric vehicles.
Benefits of Cable Assemblies
Cable assemblies offer several advantages over single cables or loose wires:
Better Organization and Utilization of Space: Assemblies reduce system clutter by bundling multiple cables together, therefore optimizing spatial utilization and making cable management easier.
Improved Reliability: They enhance the reliability of a system by reducing the risk of disconnection, wear on individual cables, and general signal integrity.
Simplified Installation and Maintenance: The pre-terminated assemblies reduce time on-site for assembly, minimizing labor time and the possibility of wiring errors, while allowing fast component replacements.
Superior Signal Integrity: Assemblies are carefully designed to minimize crosstalk and electromagnetic interference for consistent impedance in high-frequency applications.
Customization Options: Assemblies can be tailored for specific needs, including customized connectors and terminations, the addition of filters or other components to provide optimum performance.
Environmental Protection: Assemblies can be designed for resisting moisture, UV light, and chemicals, suitable for numerous industrial and outdoor settings.
Manufacturing Process and Testing
Manufacturing cable assemblies is a very precise, multi-step process that requires great attention to detail and rigid quality control:
Design and Engineering: Application requirements are analyzed first, followed by the selection of cables and connectors and checking for conformance with applicable standards.
Cable Preparation: This consists of cutting cables to precise lengths, wire-end stripping, and sometimes tinning exposed conductors to further improve connection quality.
Connector Assembly: This includes various techniques like crimping, soldering, or insulation displacement connections to fasten the connectors securely.
Cable Bundling: The individual cables are arranged using twisting, braiding, or applying cable ties for proper placement.
Overmolding or Backshell Assembly: Extra protection is afforded by overmolding cables in plastic or rubber and often added with metal or plastic backshells.
Labeling and Identification: Assemblies are labeled for easy identification using printed labels, tags, or color coding to facilitate maintenance and traceability.
Testing: Rigorously tested to specifications, testing processes include continuity and resistance checks, signal integrity testing, mechanical testing, and environmental assessments.
Applications Across Industries
Cable assemblies are essential within many industries and ensure the trustworthy function of complex systems:
Automotive: Key for various applications of engine management systems, in-vehicle entertainment, and electric vehicle power distribution.
Medical Devices: Importance in diagnostic equipment and portable medical devices, ensuring operational reliability and accuracy.
Telecommunications: They are integral to network infrastructures such as cell towers, data centers, and fiber optic networks.
Renewable Energy: Essential for power generation and distribution systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines.
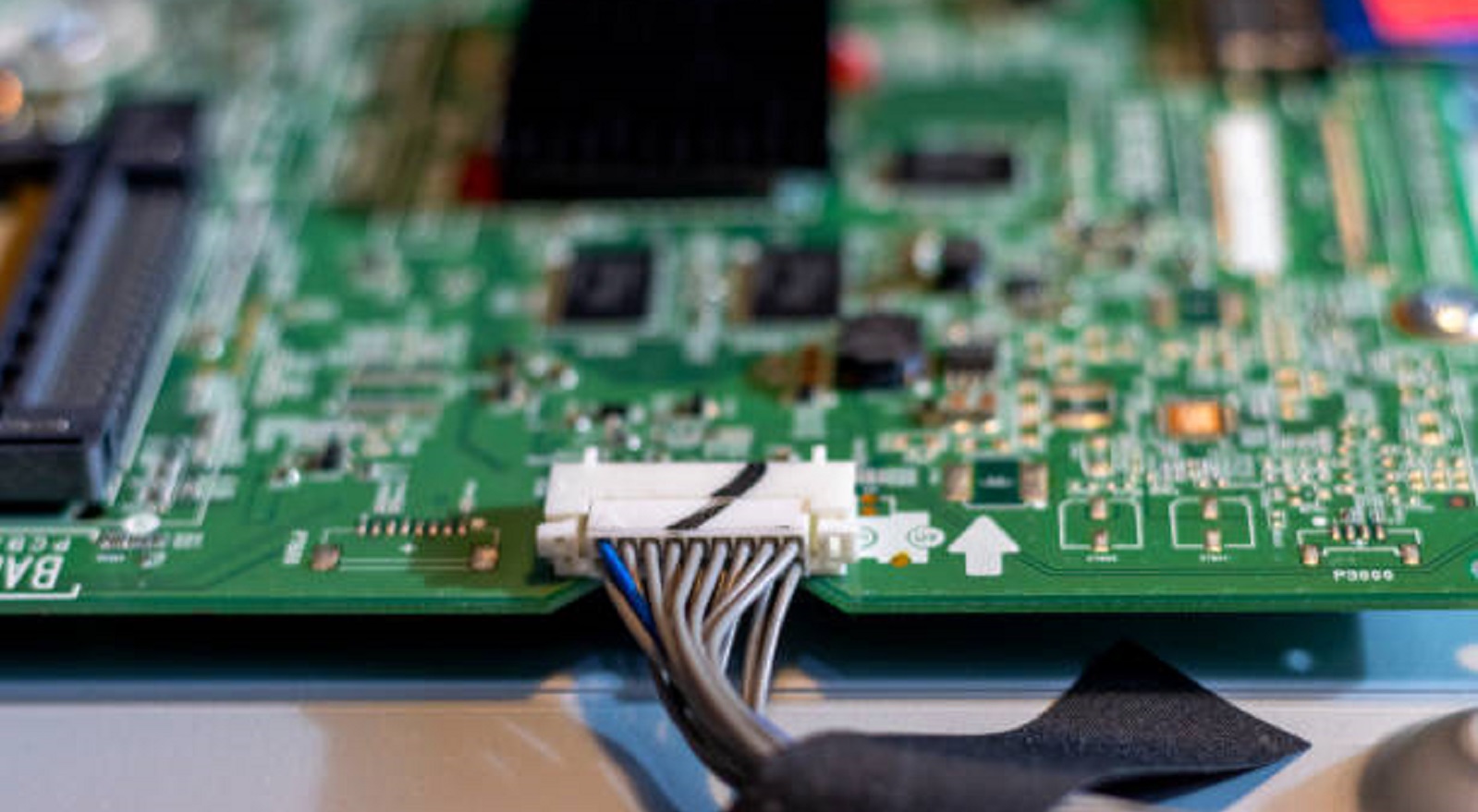

Cable assemblies are the unsung heroes of our connected world, providing vital links that will enable modern technologies to work seamlessly. As technological demands continue to evolve, cable assemblies will undoubtedly continue to play a critical role in that development, driven by the need for solid, high-performance connectivity solutions. Whether it is an off-the-shelf solution or a highly customized assembly, their types, benefits, and applications need to be understood in order to make informed decisions that enhance performance and drive innovation across industries. The investment one makes in high-quality cable assemblies is an assurance of not only a technical but also strategic advantage in making modern technology robust and efficient to meet its future challenges.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
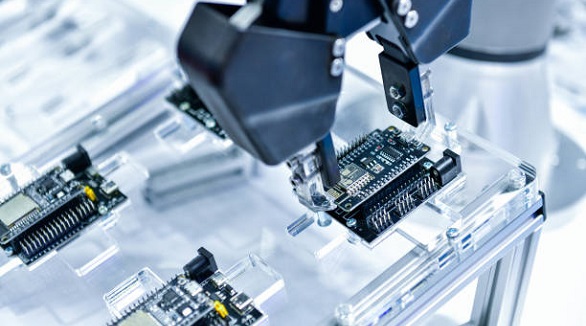
Automated PCB manufacturing enhances precision, reduces costs, and accelerates production, enabling efficient, high-quality mass production and customization, vital for industry advancement.

PCBs are essential in modern cars, enhancing performance, safety, and connectivity across systems like ADAS and infotainment, while facing design challenges.

Electronic module assembly is crucial for innovation, driven by demands for high-performance, reliable modules in fields like connectivity and electric transportation.