PCBX.com Resources
Your source for industry knowledge, news, and expert insights
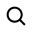
Latest Posts
Article
BGAs are vital for compact, high-functionality devices, but demand meticulous routing to overcome design challenges in reliability, manufacturability, and signal integrity.
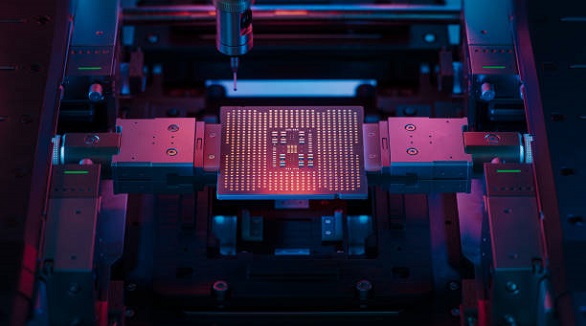
Choose the right PCB substrate based on application needs, balancing properties like Dk, Df, thermal conductivity, and cost, for optimal performance.
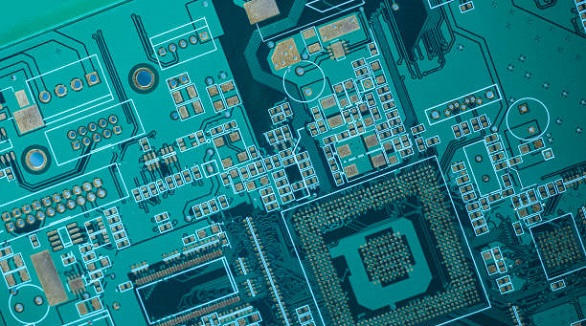
Mastering hot air rework to remove SMD chips ensures precise control, protects the PCB, and is vital for effective electronics repair and upgrades.
PCB insertion loss is crucial to managing signal attenuation in high-frequency designs, affected by materials, path length, and connectors—optimized through strategic design measures.

QFPs offer ease in inspection and modification with exposed leads, while QFNs provide compact design and superior thermal management, ideal for various applications.

PCB soldering requires precise temperature control for reliable connections. Techniques like SMT and reflow soldering use specific temperature profiles to ensure quality.

IPC Class 2 offers cost-effective reliability for non-critical electronics, while Class 3 ensures high-reliability for critical applications, at higher cost.

LED PCBs power modern lighting with efficiency and adaptability, ideal for diverse applications. Their design emphasizes thermal management, cost-effectiveness, and versatility, driving sustainable illumination solutions.