PCBX.com Resources
Your source for industry knowledge, news, and expert insights
Latest Posts
Article

Professional PCB cleaning prevents corrosion and failure, typically using 99% IPA to safely remove flux residue while maintaining component integrity.
PCBs form the foundation of electronics; standard PCBs offer cost-effective simplicity, while advanced PCBs cater to high-performance and precision requirements.
Understanding resistor power ratings in PCB design is crucial for ensuring circuit reliability, thermal efficiency, and preventing overheating through strategic layout and derating.
Choosing between clean and no-clean flux impacts PCB assembly efficiency and reliability. Clean flux suits high-stakes scenarios; no-clean excels in mass production.
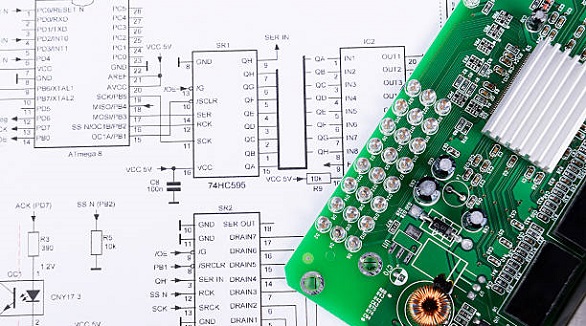
Understanding electrical schematics is essential for electronics professionals, as it connects design, testing, and production processes, facilitating effective PCB implementation.
PCB panelization improves productivity, reduces costs, and facilitates automation by assembling several smaller PCBs into one large panel, ensuring uniformity.
PCB routing is crucial for transforming schematics into functional layouts by ensuring electrical connectivity, signal integrity, and manufacturability amidst evolving design challenges.
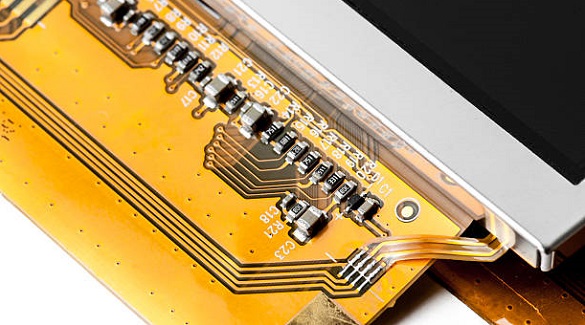
The LCD PCB interface is crucial for efficient, reliable displays, connecting control circuits to the display and impacting device performance and user experience.